Precompiled¶
Precompiled合约提供一种使用C++编写合约的方法,合约逻辑与数据分离,相比于solidity合约具有更好的性能,可以通过修改底层代码实现合约升级。
1. Precompiled合约与Solidity合约对比¶
||Precompiled合约|Solidity合约| |:—|:—|:—| |地址|固定地址,代码中定义|部署时确定| |合约代码|数据与合约分离,可升级|不可更改| |执行|C++底层执行,性能更高,可实现并行|EVM虚拟机|
2. 模块架构¶
Precompiled的架构如下图所示:
- 区块验证器在执行交易的时候会根据被调用合约的地址来判断类型。地址1-4表示以太坊预编译合约,地址0x1000-0x10000是C++预编译合约,其他地址是EVM合约。
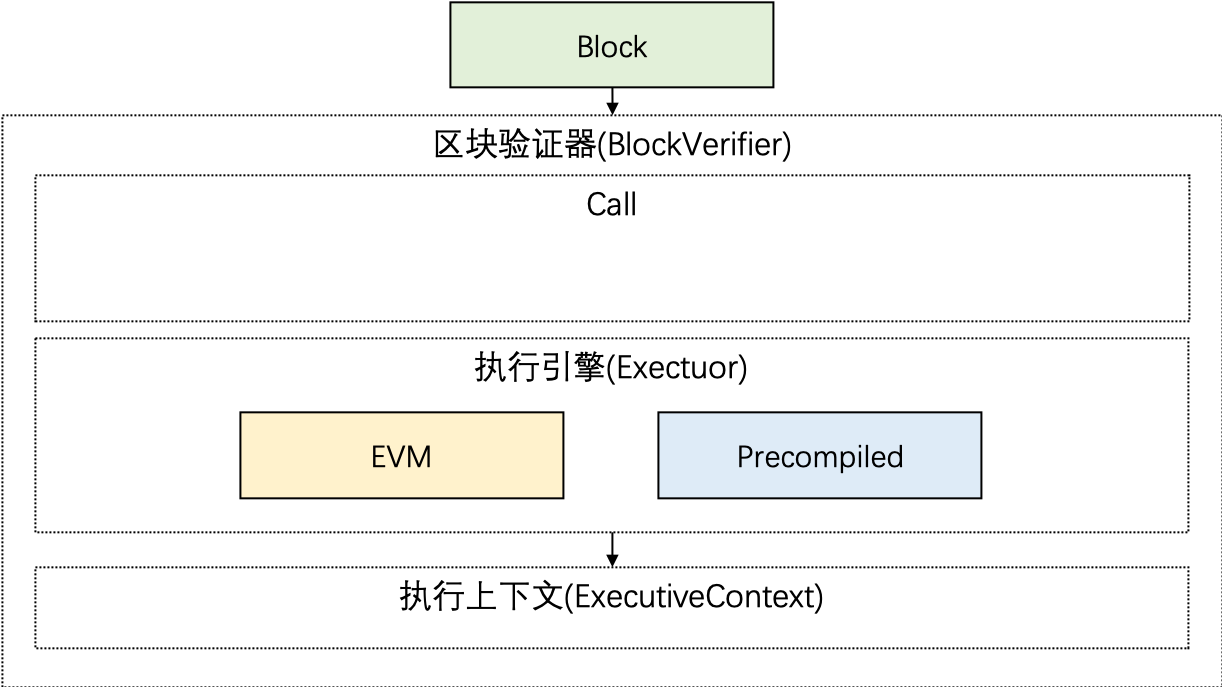 模块架构
模块架构
3. 关键流程¶
- 执行Precompiled合约时首先需要根据合约地址获取到预编译合约的对象。
- 每个预编译合约对象都会实现
call接口,预编译合约的具体逻辑在该接口中实现。 call根据交易的abi编码,获取到Function Selector和参数,然后执行对应的逻辑。
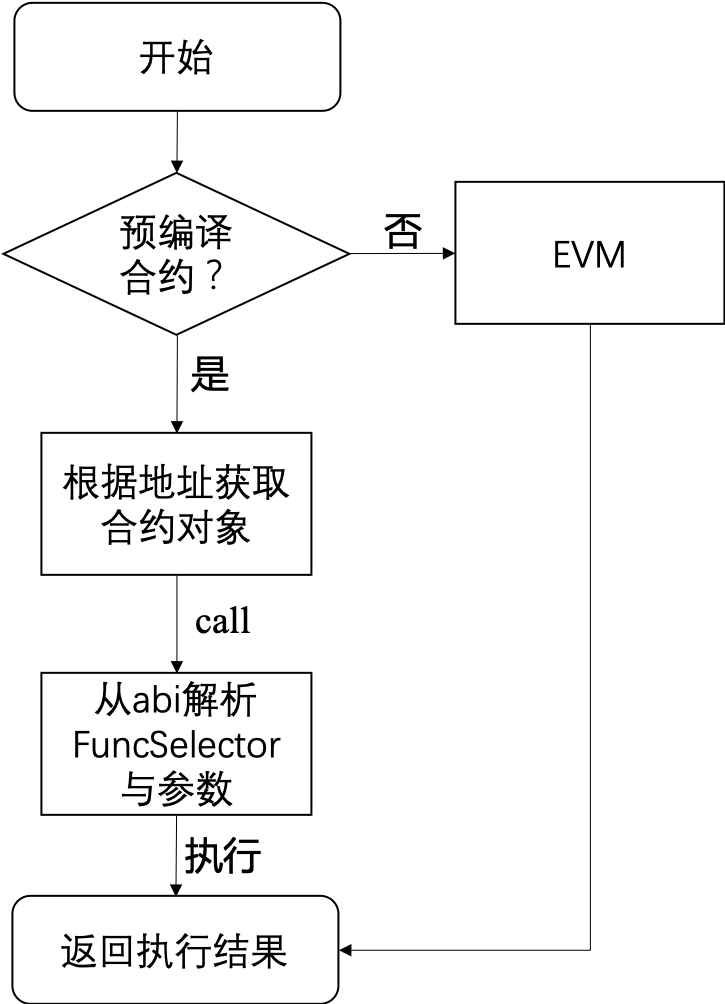
3. 接口定义¶
每个Precompiled合约都必须实现自己的call接口,接口接受三个参数,分别是ExecutiveContext执行上下文、bytesConstRef参数的abi编码和外部账户地址,其中外部账户地址用于判断是否具有写权限。
class ExecutiveContext;
class Precompiled : public std::enable_shared_from_this<Precompiled>
{
public:
typedef std::shared_ptr<Precompiled> Ptr;
virtual ~Precompiled(){};
virtual std::string toString(std::shared_ptr<ExecutiveContext>) { return ""; }
virtual bytes call(std::shared_ptr<ExecutiveContext> context, bytesConstRef param,
Address const& origin = Address()) = 0;
virtual uint32_t getParamFunc(bytesConstRef param);
virtual uint32_t getFuncSelector(std::string const& _functionName);
virtual bytesConstRef getParamData(bytesConstRef param);
protected:
std::map<std::string, uint32_t> name2Selector;
std::shared_ptr<dev::storage::Table> openTable(
std::shared_ptr<dev::blockverifier::ExecutiveContext> context,
const std::string& tableName);
};